Fire management and the law
Who is the governing body for bushfire management in South Australia?
South Australian Country Fire Service (CFS) is SA’s bushfire hazard leader and has primary responsibility to help landowners to understand their property’s vulnerability to bushfires and address their responsibilities for reducing bushfire risk.
It does this by coordinating and integrating policies, practices and strategies relating to bushfire prevention, preparedness, response and recovery activities.
As the control agency, CFS also takes the lead in responding to bushfires and directing resources and effort, including by other agencies such as the Department for Environment and Water (DEW).
DEW’s National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) has a skilled team of fire specialists with firefighting appliances which helps CFS fight bushfires on and off DEW-managed land.
This work comes under the Emergency Management Act 2004, which is supported by the State Emergency Management Plan.
Who else is responsible for bushfire management?
Managing bushfires in South Australia is governed by the Fire and Emergency Services Act 2005.
It is part of a shared responsibility with CFS, government agencies which manage land (e.g. DEW, Forestry SA and SA Water) and infrastructure, local councils, industries and private landholders.
Managing national parks and reserves
DEW has a responsibility to conserve South Australia’s biodiversity and ecosystems under the National Parks and Wildlife Act 1972 and Wilderness Protection Act 1992.
The NPWS Fire Management team manages the bushfire risk for a quarter of South Australia’s land, including more than 300 parks and reserves, taking care in choosing the most appropriate and environmentally sensitive method for the area.
There are 3 main methods used to reduce bushfire fuel, which suit different situations: mechanical removal of vegetation (such as slashing or verging), chemical knockdown (such as weed spraying), and prescribed burning.
DEW’s Fire Management Program and the law
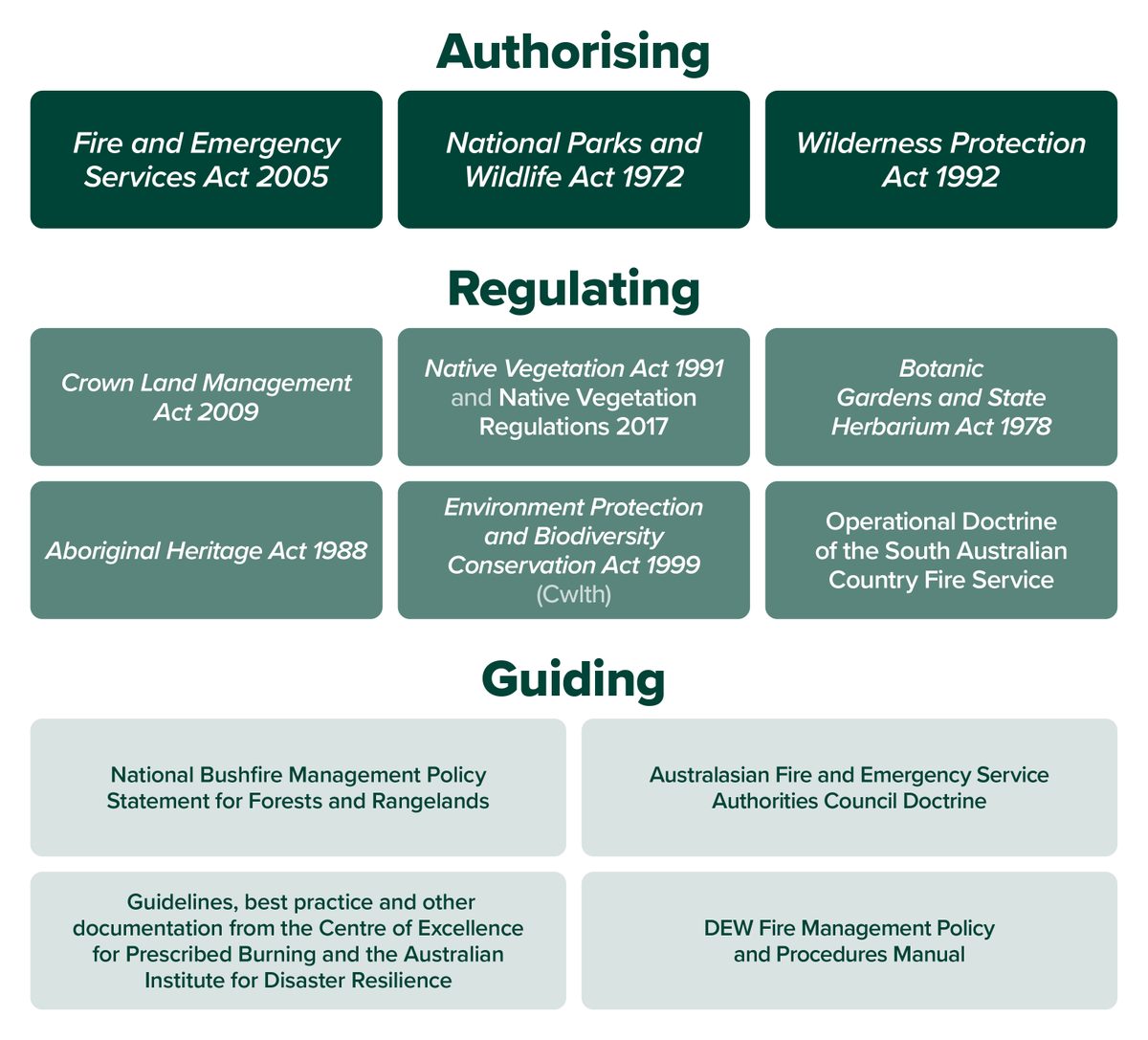
DEW’s NPWS Fire Management Program is driven by a range of State and Commonwealth Acts, regulations, and policies
See the diagram below for details
Authorising: Tells us what to do, and gives direction, to protect parks from the impact of bushfire
These Acts assign responsibility to DEW and require it to conduct fire management to protect life, property, environmental assets and cultural values: Fire and Emergency Service Act 2005 (FES Act), National Parks and Wildlife Act 1972 (NPW Act) and Wilderness Protection Act 1992 (WP Act).
Regulating: Now we know what to do, these tell us how to do it and give us other issues to consider
Ensures NPWS conducts fire management activities in line with state and national legislative and policy responsibilities.
Guiding: Here we have best practice, national consistency, and instructions for our staff
NPWS is part of a network of fire service and land management agencies across Australia that help align its fire management activities with national best practice. We continually review our Fire Management policy and procedures to keep them up to date and ensure they align with national best practice so we can achieve our objectives to a high standard.
Other things we do – bushfire recovery
The State Emergency Management Plan; Part 2 (prepared under the Emergency Management Act 2004) assigns DEW and other agencies coordinating roles in natural resources and environment recovery after disaster events.


